Core Web Vitals are user-focused metrics that will be considered as one of the new ranking signals for the website on its search engine. Here’s a brief look at the latest ranking signal and why it’s essential.
Core web vitals is the new ranking factor that Google will use to measure the user experience of the page of a website, which will determine its ranking on the search engine. If we consider that, it means the better the user experience of a page, the higher the rank. But it would be best if you also considered the other factors for ranking at the same time as well.
Some webmasters might think the tool works similar to Google’s PageSpeed Insights. However, PageSpeed insight crawls the page on the website and then creates a report with the help of software, whereas, Core Web Vitals aims to measure the user experience visitors would have on a website. Since this is calculated based on the real-world scenario, the results are often extremely accurate.
What is a good user experience?
The aim with Core Web Vitals is to offer guidance to webmasters that will help them achieve a better user experience for their website visitors. A good user experience includes the overall loading time of the page, the level of interactivity with the users and adequate visual stability of the page.
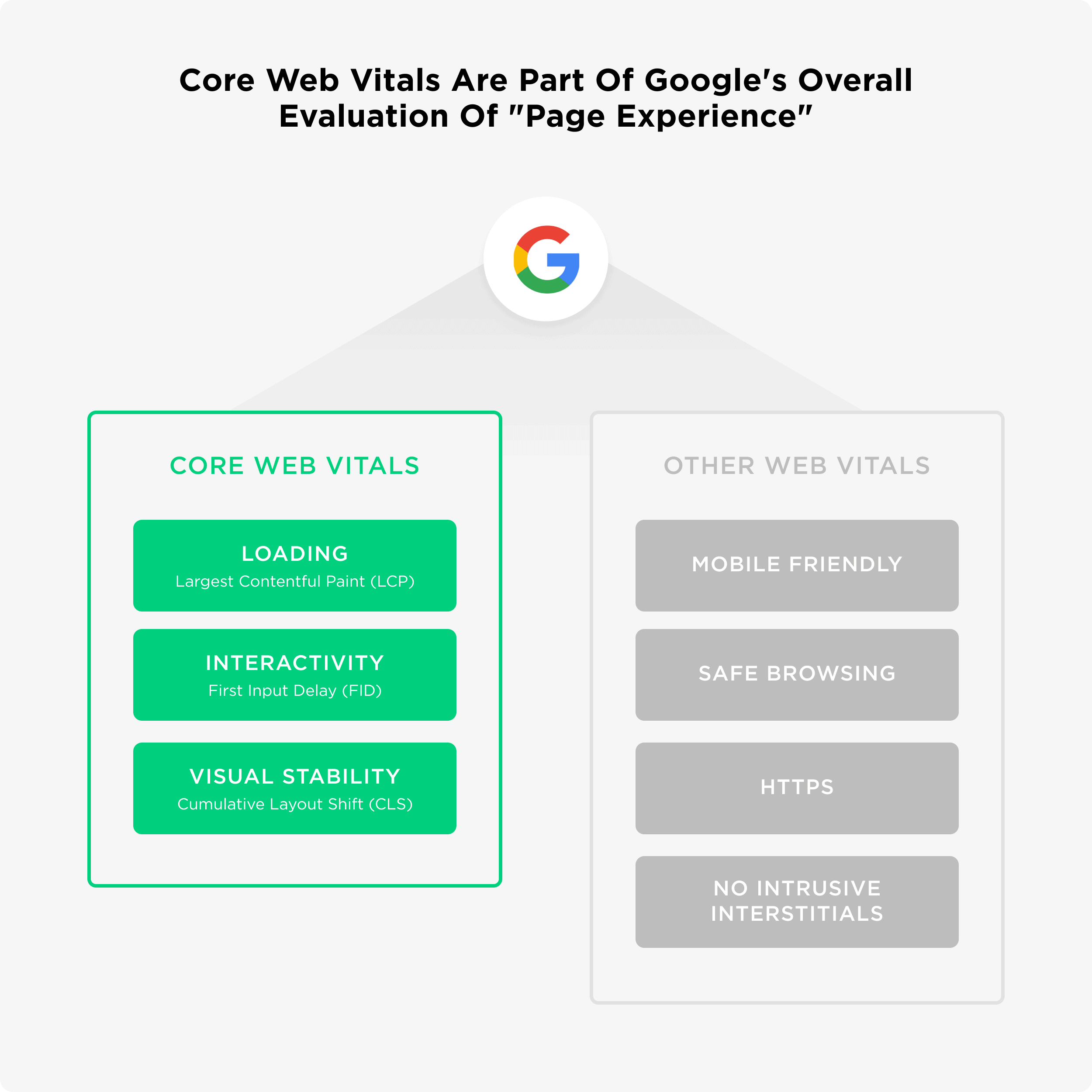
There are three Core Web Vitals metrics to keep an eye on:
LCP
Largest Contentful Paint or LCP, which is mainly associated with measuring the loading time of a web page or the exact amount of time it takes for a web page to load its content. When evaluating LCP consider the First Contentful Paint and Time to First Byte as well as they will account for more than 25% of the overall score of LCP, i.e., the time it takes for the first byte or text to appear. A speed of less than two seconds should be ideal.
FID
First Input Delay or FID, is associated with the interactivity of the page. It aims to measure the experience users have when they first interact with the page or the time when they interact with the website for the first time. It is crucial to note here that having a page with heavy JavaScript can have a negative impact on the First Input Delay. Over 15% of the overall score is dependent on interactivity.
CLS
Cumulative Layout Shift or CLS is a metric that focuses on measuring the visual stability of the web page. This implies you cannot hide the CSS code in the bottom of the page so it can count as fast load times. If there is unformatted content or moving contact on the web page, it will negatively impact your overall score. CLS or visual stability is accountable for five per cent of your overall score.
It is important to note that these metrics can change over time as more research is done on user experience, but at the time, these are the ones you should consider improving.
Where are Core Web Vitals?
To find the core web vitals, you will need to access your webmasters account. Head to Google Search Console, choose ‘Enhancements’ from the left-hand sidebar, and there you will find Core Web Vitals.
There will be two types of graphs available for each page, one for mobile traffic and one for the desktop traffic. Keep in mind; these graphs will only generate if you have an adequate amount of traffic on your website. for detailed information, you can access “Open Report” to access bar graphs with details.
Core Web Vitals can be an excellent tool for webmasters and marketers looking for methods to improve the overall performance of their website, especially emphasizing on the user experience.



![[Case Study] EduKart: Shop The Right Course By Carting It](https://www.whizsky.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/02/EduKart-218x150.png)
![[Case Study] How OnePlus Made It To Top In Indian Market](https://www.whizsky.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/02/oneplus-became-premium-brand-in-India-218x150.jpeg)








